Hypopharyngeal Cancer Overview
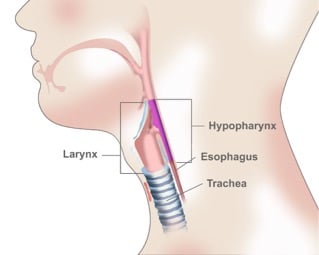
Hypopharyngeal cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the hypopharynx. It is a type of head and neck cancer.
The hypopharynx is the bottom part of the pharynx (throat). The pharynx is a hollow tube about five inches long that starts behind the nose, goes down the neck, and ends at the top of the trachea (windpipe) and esophagus (the tube that goes from the throat to the stomach). Air and food pass through the pharynx on the way to the trachea or the esophagus.
Most hypopharyngeal cancers form in squamous cells, the thin, flat cells lining the inside of the hypopharynx. The hypopharynx has three different areas. Cancer may be found in one or more of these areas.
Signs and Symptoms of Hypopharyngeal Cancer
There are several signs and symptoms that could be related to hypopharyngeal cancer; however, it is important to remember that they can also be symptoms of other diseases. See your doctor if you have:
- A lump in the neck
- Unexplained ear pain
- Pain or difficulty when swallowing
- A persistent sore throat
- Constant, persistent coughing
- Difficulty breathing
If any of these symptoms last for more than three weeks, it is a good idea to be checked by a doctor. If it is cancer, early detection can give you better treatment results.
Hypopharyngeal Cancer Risk Factors
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Risk factors of hypopharyngeal cancer may include:
- Smoking and/or chewing tobacco
- Moderate or heavy alcohol use (more than one drink a day)
- Poor nutrition
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- Genetic syndromes (inherited gene mutations)
- Workplace exposures to certain fumes and chemicals
- Gender (more common in men than women)
- Age (more common among patients age 65 and older)
- Race (more common among African Americans and Caucasians)
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Keep in mind that having a risk factor, or even several of them, does not mean that you will get hypopharyngeal cancer. Likewise, many people who do get the disease may have few or no known risk factors at all. Learn more about the diagnosis of hypopharyngeal cancer.
